Answer:
A) E = 145.6 N / C , B) y= 2,8 10-7 m with a downward direction
C) he shape of the trajectory of the two particles is to simulate a parabola,
D) F_{e} /F_{g} = 10³⁴
Step-by-step explanation:
A) For this exercise we use Newton's second law to find the acceleration of the electron, where the force is electric
F = m a
- e E = m a
a = - e E / m
with the field directed downward, the acceleration is in the vertical upward direction.
We look for how much the electron moves with kinematics, in the x direction there is no acceleration,
x axis (parallel to plates)
x = v₀ t
t = x / v₀
y axis (perpendicular to plates)
y = y₀ +
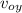 t + ½ a t²
t + ½ a t²
Let's take the zero of the system in the middle of the plates y₀ = 0, also the initial vertical velocity is zero (v_{oy} = 0) the width of the plate is known
y = ½ a t²
we substitute
y = ½ (e E /m) (x / v₀)²
y = ½ e x2 /m v₀² E
we look for the electric field
E = 2 m y v₀² / e x²
where to use this expression the length and width of the condenser must be known, suppose that the length is x = l = 1 cm = 1 10⁻² m and the width is y = 0.5 mm = 0.5 10⁻³ m
let's calculate
E = 2 9.1 10⁻³¹ 0.5 10⁻³ (1.6 10⁶)² / (1.6 10⁻¹⁹ (1 10⁻²)²)
E = 145.6 N / C
B) The electron is exchanged for a proton
Let's look for the vertical displacement, in this case as the proton has a positive charge it moves towards the bottom of the plates
y = ½ e x² / m v₀² E
y = ½ 1.6 10⁻¹⁹ 1 10⁻⁴ / (1.67 10⁻²⁷ (1.6 10⁶)² 145.6
y = 28.4375 10⁻⁸ m
since the distance between the plates is 0.5 10-3 m, the proton passes the condensate because its deflection is very small
In summary, its displacement is y= 2,8 10-7 m and with a downward direction (the same direction of the electric field)
C) The shape of the trajectory of the two particles is to simulate a parabola, but one for having a negative charge (electron) the force is upwards and the other for having a positive charge (proton) the trajectory is downwards
D) The force of gravity
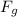 = G m M / R²
= G m M / R²
electron
Between the electron and the positive charges of the conducting plate
F_{g}= 6.67 10⁻¹¹ 1.67 10⁻²⁷ 9.1 10⁻³¹ / (0.5 10⁻³)²
F_{g} = 4.1 10⁻⁵¹ N
electric force
F_{e} = -e E
F_{e} = - 1.6 10⁻¹⁹ 145.6
F_{e} = 2.3 10⁻¹⁷ N
let's look for the reason between these two forces
F_{e} / F_{g} = 2.3 10⁻¹⁷ / 4.1 10⁻⁵¹
F_{e} /F_{g} = 10³⁴
We see that the electric force is many orders of magnitude higher than the gravitational force.