Answer:
(1) 0.04 ohms (2) 55 ohms (3) 13 volt
Step-by-step explanation:
(1) The resistance of an electric device is 40,000 microhms.
We need to convert it into ohms.
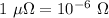
To covert 40,000 microhms to ohms, multiply 40,000 and 10⁻⁶ as follows :
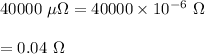
(2) Voltage used, V = 110 V
Current, I = 2 A
We need to find the resistance of the iron. Using Ohms law to find it as follows :
V = IR, where R is resistance
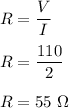
(3) Current, I = 0.2 A
Resistance, R = 65 ohms
We need to find the applied voltage in the circuit. Using Ohms law to find it as follows :
V=IR
V = 0.2 × 65
V = 13 volt