Answer:
The grapefruit dropped 2.54 m and hit the ground at 7.06 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Free Fall Motion
A free-falling object falls under the sole influence of gravity. Any object that is being acted upon only by the force of gravity is said to be in a state of free fall. Free-falling objects do not encounter air resistance.
If an object is dropped from rest in a free-falling motion, it falls with a constant acceleration called the acceleration of gravity, which value is
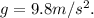
The final velocity of a free-falling object after a time t is given by:
vf=g.t
The distance traveled by a dropped object is:
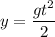
Given a grapefruit free falls from a tree and hits the ground t=0.72 s later, we can calculate the height it fell from:
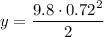
y = 2.54 m
The final speed is computed below:
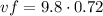
vf = 7.06 m/s
The grapefruit dropped 2.54 m and hit the ground at 7.06 m/s