Answer:
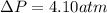
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, since the ideal gas equation is used under the assumption of no interaction between molecules and perfectly sphere-shaped molecules but the van der Waals equation actually includes those effects, we can compute each pressure as shown below, considering the temperature in kelvins (22.3+273.15=295.45K):
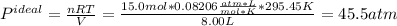
Next, since the VdW equation requires the molar volume, we proceed as shown below:
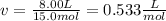
Now, we use its definition:
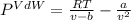
Thus, by plugging in we obtain:
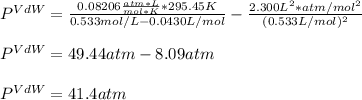
Thus, the pressure difference is:
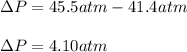
Best regards!