The balanced equation for the reaction of potassium iodide with lead (II) nitrate to form lead (II) iodide is:
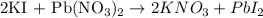
To calculate the percent yield, we first need to calculate the theoretical yield. The molar mass of KI is approximately 166 g/mol and that of PbI2 is approximately 461 g/mol.
- The first ratio used is the stoichiometric ratio from the balanced equation, which is 2 moles of KI to 1 mole of PbI2.
- The second ratio is the conversion of grams of KI to moles using its molar mass. From 20 g of KI, we get approximately 0.12 moles of KI.
- The third ratio is the conversion of moles of PbI2 to grams using its molar mass. From 0.12 moles of PbI2, we get approximately 27.77 g of PbI2.
The percent yield is then calculated as the ratio of the actual yield (15 g) to the theoretical yield (27.77 g), multiplied by 100:
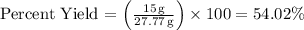
So, the percent yield of the experiment is approximately 54.02%.