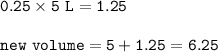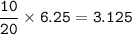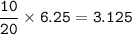The volume of NO₂=6.25 L
Further explanation
Avogadro's stated :
In the same T,P and V, the gas contains the same number of molecules
So the ratio of gas volume = the ratio of gas moles
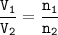
the volume of each gas (in a container of volume 10L) :
Total mol=10+10+20=40 mol
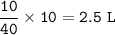
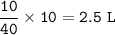
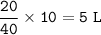
NO₂ (has increased by 25%) :