Answer:
0.758 V.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, case when we include the effect of concentration on an electrochemical cell, we need to consider the Nerst equation at 25 °C:
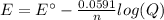
Whereas n stands for the number of moles of transferred electrons and Q the reaction quotient relating the concentration of the oxidized species over the concentration of the reduced species. In such a way, we can write the undergoing half-reactions in the cell, considering the iron's one is reversed because it has the most positive standard potential so it tends to reduction:
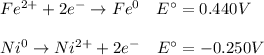
It means that the concentration of the oxidized species is 0.002 M (that of nickel), that of the reduced species is 0.40 M and there are two moles of transferred electrons; therefore, the generated potential turns out:
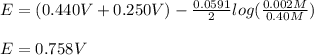
Beat regards!