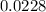Answer:
The probability is
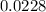
Explanation:
Let's start by defining the random variable
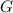 as :
as :
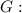 '' The amount of gasoline sold each month to customers at Bob's Exxon station in downtown Navasota ''
'' The amount of gasoline sold each month to customers at Bob's Exxon station in downtown Navasota ''
Therefore, if
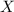 is a continuous random variable that has a normal distribution, we write
is a continuous random variable that has a normal distribution, we write
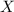 ~
~
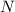 ( μ , σ )
( μ , σ )
Where ''μ'' is the mean and ''σ'' is the standard deviation.
For the random variable
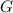 we write :
we write :
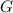 ~
~
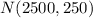
We need to find
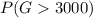
In order to calculate this, we are going to standardize the variable. This means, finding the equivalent probability in a normal random variable
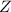 ~
~
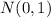
We perform this because the random variable
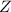 ~
~
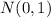 is tabulated in any book or either you can find the table on Internet.
is tabulated in any book or either you can find the table on Internet.
To standardize the variable we need to subtract the mean and then divide by the standard deviation ⇒
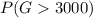 ⇒ P[ (G - μ) / σ >
⇒ P[ (G - μ) / σ >
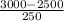 ] ⇒
] ⇒
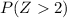
Because (G - μ) / σ ~
Finally,
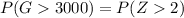 ⇒
⇒
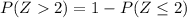 = 1 - Φ(2)
= 1 - Φ(2)
Where '' Ф(x) =
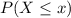 '' represents the cumulative function of
'' represents the cumulative function of
Looking for Φ(2) in any table,
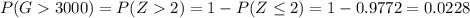 ≅ %2.28
≅ %2.28
We found out that the probability is