Answer:
1. pH = 1.23.
2.
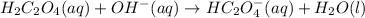
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
1. In this case, for the ionization of H2C2O4, we can write:
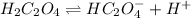
It means, that if it is forming a buffer solution with its conjugate base in the form of KHC2O4, we can compute the pH based on the Henderson-Hasselbach equation:
![pH=pKa+log(([base])/([acid]) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/8dmrsjloj30y2yhkiycsj9lw9h9a6w3h5m.png)
Whereas the pKa is:
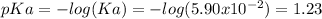
The concentration of the base is 0.347 M and the concentration of the acid is 0.347 M as well, as seen on the statement; thus, the pH is:
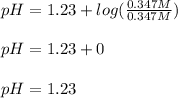
2. Now, since the addition of KOH directly consumes 0.070 moles of acid, we can compute the remaining moles as follows:
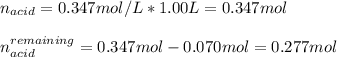
It means that the acid remains in excess yet more base is yielded due to the effect of the OH ions provided by the KOH; therefore, the undergone chemical reaction is:
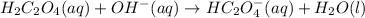
Which is also shown in net ionic notation.
Best regards!