Answer:
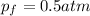
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, since the reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen produces ammonia:
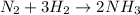
We can compute the volume of the container by using the ideal gas law at STP (1 atm and 273.15 K):
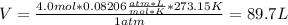
Next, since nitrogen and hydrogen are in a 1:3 mole ratio, we understand all the nitrogen and hydrogen are consumed and only ammonia remains at the end of the reaction in the following amount:
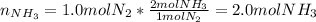
Thus, the final pressure turns out:

Best regards!