Answer:
Explanation:
From the given information:
The null and the alternative hypothesis can be well written as:
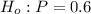
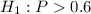
Given that:
n = 200
x = 135
Alpha ∝ = 0.05 level of significance
Then;
⇒
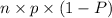
= 200 × 0.6 × (1 -0.6)
= 200 × 0.6 × 0.4
= 48 ≥ 10
The sample proportion
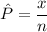
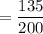
= 0.675
The test statistics
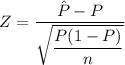
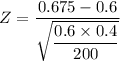
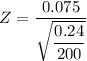
Z = 2.165
The P-value = P(Z > 2.165)
= 1 - P(Z < 2.165)
From the z tables
= 1 - 0.9848
= 0.0152
Reject the null hypothesis since P-Value is lesser than alpha. ( i.e. 0.0152 < 0.05).
Thus, there is enough evidence to conclude that the value of the population proportion is greater than 0.6