Given:
Initial Volume
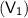 = 11.2 L
= 11.2 L
Initial Pressure
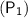 = 0.860 atm
= 0.860 atm
Final Volume
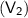 = 15.0 L
= 15.0 L
To Find:
Final Pressure
Concept/Theory:

"At constant temperature, the pressure of a fixed amount of gas varies inversely with the volume of the gas."
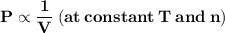
It can be also stated as "At constant temperature, the product of pressure and volume of fixed amount of a gas remains constant."
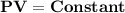
If the initial pressure and volume of a fixed amount of gas at constant temperature are
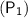 &
&
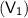 and final pressure of the gas is
and final pressure of the gas is
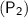 and volume occupied is
and volume occupied is
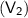 , then according to Boyle's law;
, then according to Boyle's law;
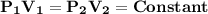
OR
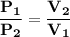
Answer:
By using Boyle's Law, we get:

 Final Pressure
Final Pressure
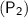 = 0.642 atm
= 0.642 atm