Answer: Yes, Mean Value Theorem for Integrals applies for the function
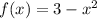 and values of x are 1 and -1
and values of x are 1 and -1
Explanation: Mean Value Theorem for Integrals states that if a function is continuous on a closed interval, there is a value c on the interval such that
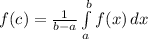
where a and b are the closed interval given
As the graph of
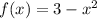 shown below, the function is continuous on the interval [0,
shown below, the function is continuous on the interval [0,
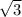 ], so the theorem applies.
], so the theorem applies.
To find the x-coordinates, first determine value of f(c) at [0,
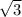 ]:
]:
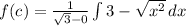
![f(c)=(1)/(√(3))[3x-(x^(3))/(3) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/wjmbv5a79l561oso5k2jrbj4kn9kjwxmne.png)
![f(c)=(1)/(√(3))[ 3√(3)-((√(3))^(3))/(3) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/z0urctdnuvwvxt4bfp5n9wdzn14uyigana.png)
![f(c)=(1)/(√(3) ) [2√(3) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/high-school/3zybe9ux2vxti5b5aqk6phv7s0g96phxq0.png)
f(c) = 2
The x-coordinates will be:
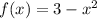
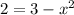
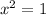
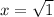
x = ±1
The values for x guaranteed by the Mean Value Theorem are +1 and -1.