Answer:
Please check the explanation.
Explanation:
As we know that the average rate of change of f(x) in the closed
interval [a, b] is
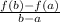
Given the interval [a, b] = [0, 4]
as
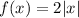
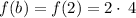 ∵
∵
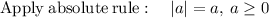
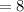
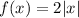
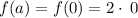 ∵
∵
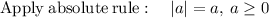
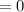
so the average rate of change :
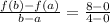
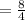
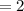
We know that a rate of change basically indicates how an output quantity changes relative to the change in the input quantity. Here, it is clear the value of y increase with the increase of input.