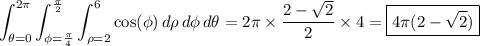Luckily, the integral is basically set up for you:
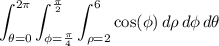
Since the limits on every variable are constant, and we can factorize
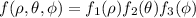 , we can similarly factorize the integrals. (This is a special case of Fubini's theorem, if I'm not mistaken.)
, we can similarly factorize the integrals. (This is a special case of Fubini's theorem, if I'm not mistaken.)
So the triple integral is equivalent to
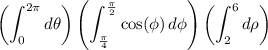
and each of these subsequent integrals are easy to compute:
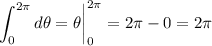
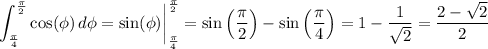
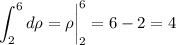
Taken together, the triple integral evaluates to