Answer:
a.
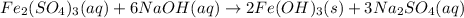
b.
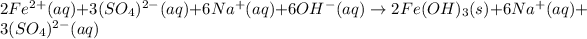
c.
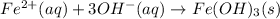
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, since the reaction between sodium hydroxide and iron (III) sulfate yields iron (III) hydroxide, an insoluble base, and sodium sulfate, a soluble salt, we can write the molecular equation as shown below:
a.
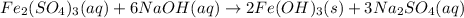
Now, for the total ionic equation, we make sure we separate the aqueous species in ions (dissociation) in order to write:
b.
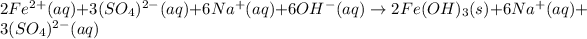
Finally, the net ionic equation comes up by cancelling out the spectator ions, those at both reactants and products sides:
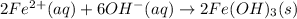
Or just:
c.
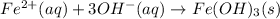
Best regards!