Answer:
i. Rotate
ii. Translates
Explanation:
Rigid transformations are the methods required in which the orientation, dimension, position, or size of a given figure can be transformed. Some types of rigid transformation are: rotation, translation, reflection, etc.
From the given question, the two rigid transformation procedure required for Madison to prove that ΔABD ≅ ΔCDB by rigid transformations are: rotation and translation.
Madison decides to rotate ΔABD
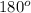 about point B to create triangle A'B'D'. Next she translates A'B'D' along diagonal BD until point B' from ΔA'B'D' lines up with point d from ΔCDB.
about point B to create triangle A'B'D'. Next she translates A'B'D' along diagonal BD until point B' from ΔA'B'D' lines up with point d from ΔCDB.
Therefore,
ΔABD ≅ ΔCDB