Answer:
Explanation:
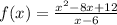
VERTICAL ASYMPTOTES
The line x = L is a vertical asymptote of the function
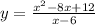
, if the limit of the function (one-sided) at this point is infinite.
In other words, it means that possible points are points where the denominator equals 0 or doesn't exist.
So, find the points where the denominator equals 0 and check them.
x=6, check:
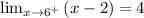
Since the limit is finite, check another limit.
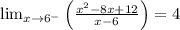
Since the limit is finite, then x=6 is not a vertical asymptote.
HORIZONTAL ASYMPTOTES
Line y=L is a horizontal asymptote of the function y=f(x), if either
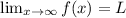
or
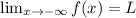 , and L is finite.
, and L is finite.
Calculate the limits:
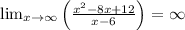
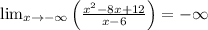
Thus, there are no horizontal asymptotes.
SLANT ASYMPTOTES
Do polynomial long division
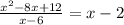 Thus, the slant asymptote is y=x−2.
Thus, the slant asymptote is y=x−2.
Answer
No vertical asymptotes.
No horizontal asymptotes.
Slant asymptote: y=x−2