Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
The chemical equation for the reaction is:
Br2(g) ⇌ 2Br(g)
Initially 0.0345M 0.0416M
![Q_C = ([Br]^2)/([Br_2]) = ((0.0416)^2)/((0.0345))= 0.05016](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/vo5mhxgwhrplkdrih7yqkl4wea0xltsxc0.png)
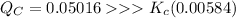
Thus, the given reaction will proceed in the backward direction
The I.C.E table is as follows:
Br2(g) ⇌ 2Br(g)
I 0.0345 0.0416
C +x -2x
E (0.0345+x) (0.0416 -2x)
![K_c = ([Br]^2)/([Br_2]) = ((0.0416-2x)^2)/((0.0345+x)) = 0.00584](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/pdnt8amk14bat51ocxoddx83czygrygaje.png)
= 0.00173056 - 0.0832x - 0.0832x + 4x² = 0.00584 (0.0345 +x)
= 0.00173056 - 0.166x + 4x² = 2.0148× 10⁻⁴ + 0.00584x
= 0.00173056 - 2.0148× 10⁻⁴ - 0.166x - 0.00584x + 4x²
= 0.00152908 - 0.17184x + 4x²
Solving by using Quadratic formula
x = 0.03038 or 0.0126
For x = 0.03038
At equilibrium
[Br₂] = (0.0345 + 0.03038) = 0.06488 M
[Br] = (0.0416 -2(0.03038)) = - 0.01916 M
Since we have a negative value for [Br], we discard the value for x
For x = 0.0126
At equilibrium
[Br₂] = (0.0345 + 0.0126) = 0.0471 M
[Br] = (0.0416 -2(0.0126)) = 0.0164 M