Answer:
The instantaneous velocity at t = 1 will be:
Explanation:
Given the position of an object at a time
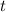
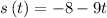
As we know that determining the derivative of the position function with respect to time t would give us the instantaneous velocity, so
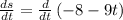
Applying the sum/difference rule:
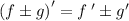
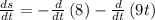
as
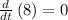 ∵
∵
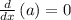
and
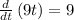 ∵
∵
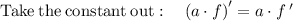 and
and
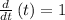
so the expression becomes
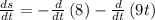
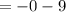

As the derivative is constant.
Therefore, the instantaneous velocity at t = 1 will be: