Answer:
A) 1.96 * 10^-8 J
B) 2.55 * 10^-7 m
Step-by-step explanation:
A) calculate the kinetic energy in eV of the recoiling Cs atom
we have to apply the principle of energy conservation and momentum
Initial kinetic energy of electron = 16 eV = 16 * (1.6 * 10^-19 ) J
Initial kinetic energy of atom = 0
therefore the final kinetic energy after collision ( E )
= [ 16 * ( 1.6 * 10^-19 ) ] + 0
= 1.96 * 10^-8 J
B) Determine the wavelength of the ultraviolet radiation
accelerating Voltage = 4.87 V
K.E = eV = 1.6 * 10^-19 * 4.87
next we will apply Planck's relationship
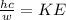 --------- ( 1 )
--------- ( 1 )
w = wavelength
h = 6.64 * 10^-34 J-S ( Planck's constant )
c = 3 * 10 ^8 m/sec ( speed of light )
KE = 1.6 * 10^-19 * 4.87
substitute given values into equation 1 above
w ( wavelength ) = 2.55 * 10^-7 m