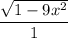Answer:
Explanation:
If we consider a triangle with the length of the hypotenuse being equal to 1 and the length of the opposite side = 3x.
However, recall that in a right-angle triangle;
SIne = opposite/hypothenuse
Thus; let the angle facing the opposite be y
Then;
SIn y = 3x/1
Sin y = 3x
Thus, y = arcsin (3x)
Now; to find cos(arcsin 3x)
Recall that:
Cosine = adjacent/hypotenuse
Now, using Pythagoras rule;
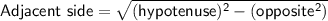
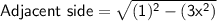
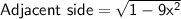
cos(arcsin 3x) = cos y = adjacent side/hypotenuse =
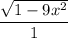
cos(arcsin 3x) =