Answer:
The space available will vary between 800 GB (100%) and 400 GB (50%) of the total disks, depending on the RAID level.
The OS will handle the RAID as a single disk.
Step-by-step explanation:
Each RAID level implements parity and redundancy in a different way, so the amount of disks used for this extra information will reduce the space available for actual storage.
Usual RAID levels are:
RAID 0: does not implement any redundancy or parity, so you will have available 100% of the total storage: 8 x 100 GB = 800 GB
RAID 1: Duplicates all the information in one disk to a second disk. Space is reduced in half: 400 GB
RAID 5: Uses the equivalent of 1 disk of parity data distributed evenly on each disk, meaning the space available is
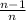 of the total disks:
of the total disks:
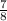 of 800 GB = 700 GB
of 800 GB = 700 GB
Writting and reading the information on a RAID storage is handled by a raid controller, either implemented in hardware or software. The OS will "see" a single disk and will read or write information as usual.