Answer: Partial pressures are 0.6 MPa for nitrogen gas and 0.4 MPa for carbon dioxide.
Step-by-step explanation: Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure states when there is a mixture of gases the total pressure is the sum of the pressure of each individual gas:
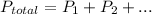
The proportion of each individual gas in the total pressure is expressed in terms of mole fraction:
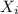 = moles of a gas / total number moles of gas
= moles of a gas / total number moles of gas
The rigid tank has total pressure of 1MPa.
molar mass = 14g/mol
mass in the tank = 2000g
number of moles in the tank:
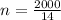 = 142.85mols
= 142.85mols
molar mass = 44g/mol
mass in the tank = 4000g
number of moles in the tank:
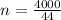 = 90.91mols
= 90.91mols
Total number of moles: 142.85 + 90.91 = 233.76 mols
To calculate partial pressure:
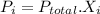
For Nitrogen gas:
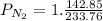
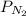 = 0.6
= 0.6
For Carbon Dioxide:
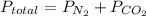
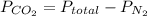
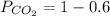
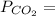 0.4
0.4
Partial pressures for N₂ and CO₂ in a rigid tank are 0.6MPa and 0.4MPa, respectively.