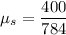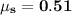Answer:
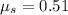
Step-by-step explanation:
Coefficient of friction
The static coefficient of friction is a measure of the force needed to start moving an object from rest along a rough surface.
It's calculated as:
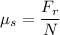
Where Fr is the friction force and N is the normal force exerted by the surface over the object.
In the absence of any other vertical force, the normal is equal to the weight of the object:
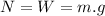
The box has a mass of m=80 Kg, thus the normal force is:
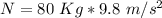
N = 784 N
The student needs to push with a force of 400 N to make the box move. That is the force that barely outcomes the friction force. Thus:
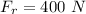
Calculating the coefficient: