Answer:
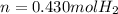
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, considering the partial Dalton's law of partial pressures, we can notice that the total pressure equals the pressure of steam and the pressure of hydrogen, which can be determined as shown below:
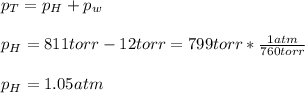
Thus, by using the ideal gas law, we can compute the moles of hydrogen as shown below:
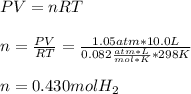
Best regards!