Answer:
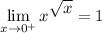
General Formulas and Concepts:
Algebra II
- Natural logarithms ln and Euler's number e
- Logarithmic Property [Exponential]:
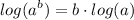
Calculus
Limits
- Right-Side Limit:
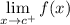
- Left-Side Limit:
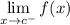
Limit Rule [Variable Direct Substitution]:
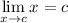
L’Hopital’s Rule:
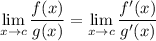
Differentiation
- Derivatives
- Derivative Notation
Basic Power Rule:
- f(x) = cxⁿ
- f’(x) = c·nxⁿ⁻¹
Explanation:
We are given the following limit:
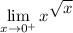
Substituting in x = 0 using the limit rule, we have an indeterminate form:
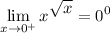
We need to rewrite this indeterminate form to another form to use L'Hopital's Rule. Let's set our limit as a function:
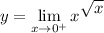
Take the ln of both sides:
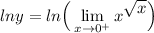
Rewrite the limit by including the ln in the inside:
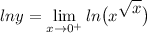
Rewrite the limit once more using logarithmic properties:
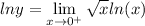
Rewrite the limit again:
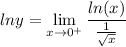
Substitute in x = 0 again using the limit rule, we have an indeterminate form in which we can use L'Hopital's Rule:
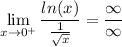
Apply L'Hopital's Rule:
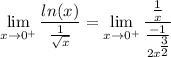
Simplify:
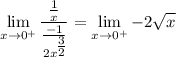
Redefine the limit:
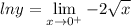
Substitute in x = 0 once more using the limit rule:
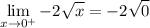
Evaluating it, we have:
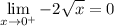
Substitute in the limit value:
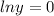
e both sides:
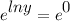
Simplify:
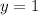
And we have our final answer.
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Limits