Answer:
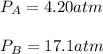
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, since the equation for the ideal gas is:
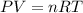
For each gas, given the total volume, temperature (28.1+273.15=301.25K) and moles, we can easily compute the partial pressure as shown below:

Best regards!