Answer:
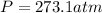
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, since the Van der Waals' equation is used in order to analyze a gas slightly deviated from the ideal condition and is defined as:
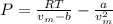
Whereas a and b for oxygen are 0.0318 L/mol and 1.36 atm*L²/mol² respectively and represent the effective volume and the eventual interactions among the gas molecules. Moreover, the molar volume, vm, is:
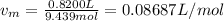
Thus, the required pressure turns out:

Best regards!