The volume of 0.258 M
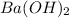 required to react completely with 3.00 g sulfur is 0.364 L
required to react completely with 3.00 g sulfur is 0.364 L
How to calculate the volume of
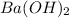 ?
?
First, we shall calculate the volume of
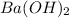 that took part in the reaction. This is shown below:
that took part in the reaction. This is shown below:
- Mass of S (m) = 3.00 g
- Molar mass of S (M) = 32 g/mol
- Mole of S = m / M = 3 / 32 = 0.094 mole
- Mole of
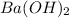 =?
=?
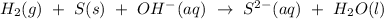
From the balanced equation above,
1 mole of S reacted with 1 mole of
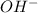
Therefore,
0.094 mole of S will also react with 0.094 mole of
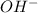
Thus, the mole of
 that took in the reaction is 0.094 mole
that took in the reaction is 0.094 mole
Finally, we shall calculate the volume of
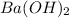 that is required for the reaction. Details below:
that is required for the reaction. Details below:
- Mole of
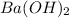 = 0.094 mole
= 0.094 mole - Molarity of
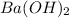 = 0.258 M
= 0.258 M - Volume of
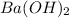 =?
=?
Volume of
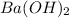 = Mole / molarity
= Mole / molarity
= 0.094 / 0.258
= 0.364 L