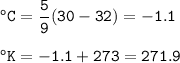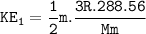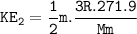KE at 30°F=0.942 KE at 60°F
Further explanation
The average kinetic energy value is only affected by temperature changes. The higher the temperature, the average kinetic energy of the molecule increases
This molecule is very small when compared to the distance between molecules, so the volume of gas contains mostly empty space
Gas particles move randomly (both speed and direction , as vector)
Average velocities of gases can be expressed as root-mean-square averages. (V rms)
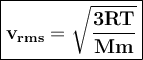
R = gas constant, T = temperature, Mm = molar mass of the gas particles
Kinetic energy :
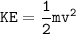
The temperature outside is 60°F
Convert to Celcius and Kelvin
°C = 5/9 (°F-32)
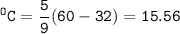
°K = °C + 273
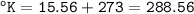
For 30°F :