Answer:
0.23J/g°C
Step-by-step explanation:
Given parameters:
Mass of sample = 135g
Amount of heat = 2.5kJ
Initial temperature = 19.5°c
Final temperature = 100°C
Unknown:
Specific heat capacity of the metal = ?
Solution:
The specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of heat required to the raise the temperature of 1g of the substance by 1°C.
H = m C (T₂ - T₁ )
H is the amount of heat
m is the mass
C is the specific heat capacity
T₂ is the final temperature
T₁ is the initial temperature;
2.5 x 10³ = 135 x C x (100 - 19.5)
2500 = 10867.5C
C =
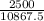 = 0.23J/g°C
= 0.23J/g°C