Answer:
The velocity of the skier at the bottom of the ramp is approximately 26.288 meters per second.
Step-by-step explanation:
We can determine the final velocity of the skier at the bottom of the ramp by Principle of Energy Conservation and Work-Energy Theorem, whose model is:
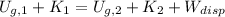 (1)
(1)
Where:
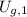 ,
,
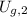 - Initial and final gravitational potential energy, measured in joules.
- Initial and final gravitational potential energy, measured in joules.
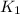 ,
,
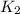 - Initial and final translational kinetic energy, measured in joules.
- Initial and final translational kinetic energy, measured in joules.
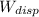 - Work dissipated by friction, measured in joules.
- Work dissipated by friction, measured in joules.
By definitions of gravitational potential and translational kinetic energy and work, we expand and simplify the model:
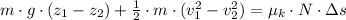 (2)
(2)
Where:
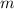 - Mass, measured in kilograms.
- Mass, measured in kilograms.
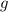 - Gravitational acceleration, measured in meters per square second.
- Gravitational acceleration, measured in meters per square second.
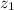 ,
,
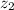 - Initial and final heights of the skier, measured in meters.
- Initial and final heights of the skier, measured in meters.
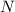 - Normal force from the incline on the skier, measured in newtons.
- Normal force from the incline on the skier, measured in newtons.
 - Distance covered by the skier, measured in meters.
- Distance covered by the skier, measured in meters.
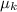 - Kinetic coefficient of friction, dimensionless.
- Kinetic coefficient of friction, dimensionless.
The normal force exerted on the skier and the covered distance are, respectively:
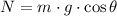 (3)
(3)
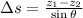 (4)
(4)
Where
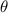 is the angle of the incline above the horizontal, measured in sexagesimal degrees.
is the angle of the incline above the horizontal, measured in sexagesimal degrees.
By applying (3) and (4) in (2), we get that:
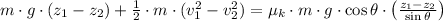
 (5)
(5)
Then, we clear the velocity of the skier at the bottom of the ramp is: (
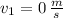 ,
,
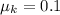 ,
,
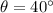 ,
,
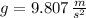 ,
,
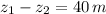 )
)
![\left[(\mu_(k))/(\tan \theta)-1 \right]\cdot g\cdot (z_(1)-z_(2)) = (1)/(2)\cdot (v_(1)^(2)-v_(2)^(2))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/wn740bh3nqmtuy5sol9olrq7zzhr78zh3b.png)
![2\cdot \left[(\mu_(k))/(\tan \theta)-1 \right]\cdot g\cdot (z_(1)-z_(2)) = v_(1)^(2)-v_(2)^(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/h5slt7sfzug4opsw5wwz93vz45apes46ie.png)
![v_(2) = \sqrt{v_(1)^(2)-2\cdot \left[(\mu_(k))/(\tan \theta)-1 \right]\cdot g\cdot (z_(1)-z_(2))}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/o0qkw3mkodvck8dv77o684ayt9c7pw3deh.png) (6)
(6)
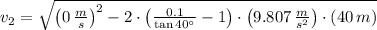
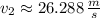
The velocity of the skier at the bottom of the ramp is approximately 26.288 meters per second.