optimizing the flash evaporator pressure for maximum efficiency in a nuclear power plant for 750 MW output requires determining state points, overall water flow rates, heat transfer, turbine flow distribution, pump power requirements, and cooling water flow rates, with consideration for specified efficiencies and temperatures, requiring iterative calculations and potentially specialized thermodynamic software.
Designing an efficient thermodynamic cycle for a nuclear power plant to produce 750 MW of electric power involves several key considerations. Let's outline the critical parameters and their calculated values:
1. State Points, Temperature, Pressure, and Entropy:
State 1 (Entering Reactor):
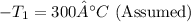
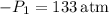
State 2 (Flash Evaporator Exit):
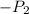 : To be determined for maximum efficiency
: To be determined for maximum efficiency
- Isenthalpic process:
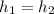
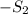 : Determine based on the known values
: Determine based on the known values
State 3 (Mixing Chamber Exit):
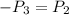
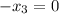
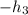 and
and
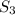 can be determined based on the known values.
can be determined based on the known values.
2. Overall Flow Rate of Water Through the Nuclear Reactor:
Calculate the overall flow rate based on the mass flow rate of steam at state 2 and the enthalpy change.
3. Heat Transfer in the Nuclear Reactor:
Calculate the heat transfer in the reactor using an energy balance.
4. % of Overall Flow Rate Passing Through the Steam Turbine:
Determine the percentage based on the mass flow rates at states 2 and 3.
5. Power Required for Condensate Pump 1:
Calculate the pump work for condensate pump 1 using the isentropic efficiency.
6. Power Required for Condensate Pump 2:
Calculate the work for condensate pump 2, assuming a similar isentropic efficiency.
7. Cooling Water Flow Rate:
Determine the cooling water flow rate based on the given condenser efficiency and the exit temperature.
Additional Considerations:
- Ensure the turbine exit quality is at least 90%.
- Consider the condenser efficiency of 93%.
- Account for the electric generator efficiency of 96%.
These calculations involve specific thermodynamic equations and may require iteration to optimize the flash evaporator pressure (P2) for maximum efficiency. Utilizing specialized thermodynamic software or consulting with a thermodynamics expert is recommended to obtain accurate and optimized results for the design of the nuclear power plant.