Answer:
8.4 N/m
Step-by-step explanation:
m = Mass of block = 4.63 gm
g = Acceleration due to gravity =
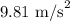
x = Displacement of spring = 0.45 cm
a = Acceleration of subject = 0.832g
k = Spring constant
Force is given by
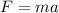
From Hooke's law
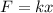
So
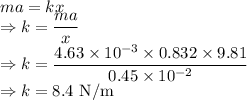
The force constant of the spring is 8.4 N/m.