Answer:
The radius of O^2- is 1.5*10^-8 cm and the radius of
Mg ^2+ is 6.2*10^-9 cm
Step-by-step explanation:
Face centered cubic : 1/8 atoms on each edges + 1/2 atoms on each face
=
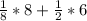 = 4 effective atoms
= 4 effective atoms
MgO have a structure like NaCl forms a lattice of FCC.
density of the lattice =
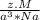
z : no of atoms
M: mass of the atoms
a: radius of the atom
Na: Avogadro's number
a^3(radius) =
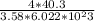
a^3 = 7.477 * 10^-23 cm^3
a = 4.21 * 10^-8 cm
Now calculating the anionic(ra O^2-) and cationic (rc Mg^2+)
in Fcc a = 2
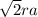
ra = 1.5*10^-8 cm
a = 2ra + 2rc
rc = a/2 -ra
rc = 6.2*10^-9 cm
The radius of O^2- is 1.5*10^-8 cm and the radius of Mg ^2+ is 6.2*10^-9 cm