Answer:
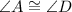
Explanation:
The Side-Angle-Side method cana only be used when information given shows that an included angle which is between two sides of a ∆, as well as the two sides of the ∆ are congruent to the included side and two sides of the other ∆.
Thus, since John already knows that
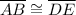 and
and
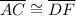 , therefore, an additional information showing that the angle between
, therefore, an additional information showing that the angle between
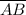 and
and
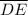 in ∆ABC is congruent to the angle between
in ∆ABC is congruent to the angle between
 and
and
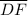 in ∆DEF.
in ∆DEF.
For John to prove that ∆ABC is congruent to ∆DEF using the Side-Angle-Side method, the additional information needed would be
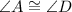 .
.
See attachment for the diagram that has been drawn with the necessary information needed for John to prove that ∆ABC is congruent to ∆DEF.