Answer:
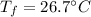
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
In this case, when two substances at different temperature are placed in contact in an isolated container, we can say that the heat lost by the hot substance is gained by the cold substance. In such a way, since granite is at 76.0 °C and water at 22.0 °C we infer granite is hot and water is cold, so we write:
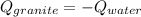
In terms of mass, specific heat and change in temperature, we write:
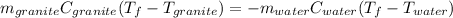
Thus, since the temperature is the same for both substance, we can solve for it as shown below:
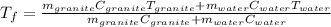
By plugging in each variable, we obtain:
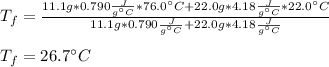
Best regards!