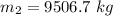Complete Question
The complete question is shown on the first uploaded image
Answer:
a
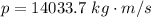
b
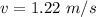
c
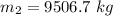
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The mass of the coal car is
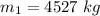
The velocity is
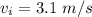
The load of coal dropped is
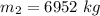
Generally the momentum of the system before the coal is added is mathematically represented as
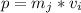
=>
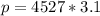
=>
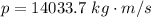
Generally from the law of momentum conservation is mathematically represented as
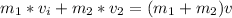
Here
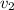 is the velocity of the load before it is dropped and the value is 0 m/s
is the velocity of the load before it is dropped and the value is 0 m/s
So
=>
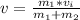
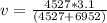
=>
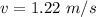
When v = 1m/s and
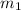 remain the same
remain the same
Then
=>
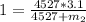
=>
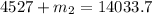
=>