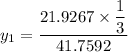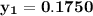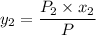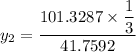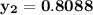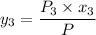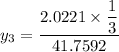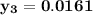Answer:
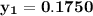
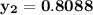
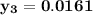
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
The temperature of the ideal solution formed by the compounds = 353K
= (353 - 273)° C
= 80° C
The data below shows the Antoine constant obtained for 1-Butanol, Benzene, and Phenol.
Compound A B C
1 - Butanol 15.3144 3212.43 182.739
Benzene 13.7819 2726.81 217.572
Phenol 14.4397 3507.80 175.400
By the application of the Antoine constant, we can find the vapor pressure of each corresponding component at the given temperature of 80° C.
The Antoine equation is expressed as:
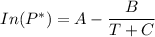
![P_1 ^* = exp \bigg [15.314 - (3212.43)/(80+182.739) \bigg ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/mr6unt9qi806okob11zcrxgmntwpldr105.png)
![P_1 ^* = exp \bigg [15.314 - (3212.43)/(262.739) \bigg ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/gv9oaixrkkb6zq442kuj29gddulvq0cigc.png)
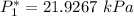
![P_2^* = exp \bigg [13.7819 - (2726.81)/(80+217.572) \bigg ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/b6enowava7b9iau71niqk6vnv2r0wtm4pn.png)
![P_2^* = exp \bigg [13.7819 - (2726.81)/(297.572) \bigg ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/ek6wp97e7a1tfbjxuthx5l93ewfwkuokm7.png)
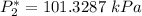
![P_3^* = exp \bigg [14.4387 - (3507.80)/(80+175.400) \bigg ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/k9e1ze1wlrl0aii1qhned7602p5jr1n6gt.png)
![P_3^* = exp \bigg [14.4387 - (3507.80)/(255.4) \bigg ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/7kgpmx7vusbnwegtf7u0h3yk4wrd4cyzd4.png)
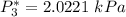
However, since the ideal solution has equimolar composition.
Then:
component (1) = 1 mole ,
component (2) = 1 mole,
component (3) = 1 mole,
The total mole = 1 + 1 + 1 = 3,
Thus, mole fraction = mole of component/total mole,
mole fraction of component (1)
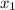 = 1/3,
= 1/3,
mole fraction of component (2)
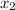 = 1/3,
= 1/3,
mole fraction of component (3)
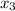 = 1/3,
= 1/3,
i.e.
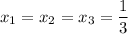
Using Raoult's law, The total pressure is computed as:
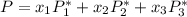
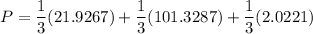
P = 41.7592 kPa
and;
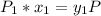
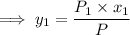
Thus: