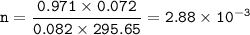a. P=0.971 atm=737.6 mmHg
b. n=2.88 x 10⁻³
Further explanation
Dalton's law of partial pressures states that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the component gases
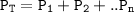
A. vapor pressure of water at 22.5 = 20.4 mmHg
Pt=P H₂ + P H₂O
758 = P H₂ + 20.4
P H₂=737.6 mmHg=0.971 atm
B.Ideal gas Law = PV=nRT
P = 0.971 atm
V = 72 ml = 0.072 L
R = 0.082 L/atm mol
T = 22.5 + 273.15 =295.65