Answer:
15300 N
Step-by-step explanation:
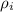 = Density of air at inlet
= Density of air at inlet
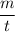 = Mass flow rate = 60 kg/s
= Mass flow rate = 60 kg/s
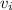 = Inlet velocity = 225 m/s
= Inlet velocity = 225 m/s
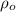 = Density of gas at outlet =
= Density of gas at outlet =
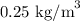
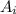 = Inlet area
= Inlet area
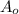 = Outlet area =
= Outlet area =
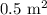
Since mass flow rate is the same in the inlet and outlet we have
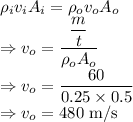
Thrust is given by
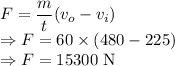
The thrust generated is 15300 N.