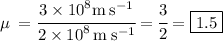Step-by-step explanation:
Snell's Law of refraction:
Refraction of light obeys the following its two laws which's snell's law.
- The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the refracted ray, all lie in the same plane.
- For a given pair of media and given colour of light, the ratio of the sine of angle of incidence i to the sine of angle of refraction r is a constant i.e.
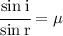
This is known as the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium. Mu is given as:
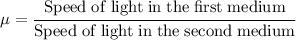
Let's take an example.
If a ray light travels from air to water,then mu = sin i/sin r is the refractive index of water with air.
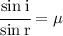
Ex.1:Ray light from air to water
- sin i = 3*10^6 m/s^1
- sin r = 2.25*10^8 m s^-1
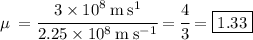
Ex.2: Ray light from Air to glass:
- sin i = 3*10^8 m s ^-1
- sin r = 2*10^8 m s^-1