Answer:
-50
Explanation:
1 - 2 + 3 - 4 + 5 - 6 + 7 - 8...99 - 100
just means,
1 - 2 = -1
3 - 4 = -1
5 - 6 = - 1
7 - 8 = - 1
99 - 100 = -1
basically, -1 + -1 + -1 + -1 + ....+ -1 or -1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - ... - 1
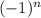
Treating Grandi's series as a divergent geometric series we may use the same algebraic methods that evaluate convergent geometric series to obtain a third value:
S = 1 − 1 − 1 + ..., so
1 − S = 1 − (1 − 1 − 1 ...) = 1 − 1 − 1 ... = S
1 - S = S
1 = 2*S
resulting in S = 1/2. The same conclusion results from calculating −S, subtracting the result from S, and solving 2S = 1
1/2 of the last term is 100 x 1/2 = 50
This because you are using 2 numbers per -1
example: 1 - 2 = -1 or 3 - 4 = -1 resulting in 50 of the -1 being subtracted