Answer:
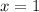 satisfies the conclusion of the Mean Value Theorem.
satisfies the conclusion of the Mean Value Theorem.
Explanation:
According to the Mean Value Theorem, a function must be continuous on
![[a,b]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/dyyh30s5r4ox0wg76shisxuulr9zptlacg.png) and differentiable on
and differentiable on
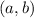 . Let
. Let
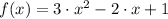 for
for
![[0, 2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/jhkas41k47bc4d5pxdlqan5s698ex315fa.png) . The function is continuous as domain of polynomial functions is the set of all real numbers.
. The function is continuous as domain of polynomial functions is the set of all real numbers.
Now, we proceed to prove that such function is differentiable, that is, that the function has a derivative for all value of
 by applying definition of differentiation:
by applying definition of differentiation:
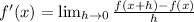 (Eq. 1)
(Eq. 1)
Where
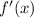 is the derivative of
is the derivative of
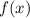 .
.
Then, we proceed to substitute all values and simplifying the resulting expression by Algebra:
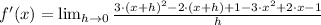
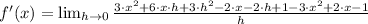
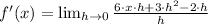
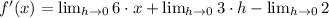
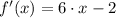
Which means that the derivative of the quadratic function is a linear function, whose domain is the set of all real numbers. Hence,
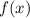 is differentiable and satisfies all hypotheses.
is differentiable and satisfies all hypotheses.
Given that
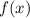 is continuous and differentiable, the following condition must be satisfied:
is continuous and differentiable, the following condition must be satisfied:
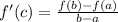 ,
,
![c\in[a,b]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/xj85xh83vrbomgpzzpdmo1o434yj50swhf.png) (Eq. 2)
(Eq. 2)
If
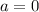 and
and
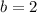 , then function evaluted at each bound is, respectively:
, then function evaluted at each bound is, respectively:
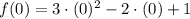
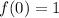
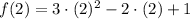
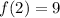
By replacing each term on (Eq. 2), we get this expanded version:
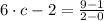
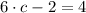
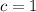
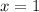 satisfies the conclusion of the Mean Value Theorem.
satisfies the conclusion of the Mean Value Theorem.