Answer:
r1 = 4 and r2 = -10 and the final equation will be C1e^4x + C2e^-10x
Explanation:
The general solution to the second order differential equation
y'' + 6y' -40y=0
substitute y= e^rx
y' = re^rx
y'' = r^2*e^rx
The equation will be
r^2*e^rx + 6r*e^rx - 40*e^rx = 0
e^rx (
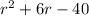 ) = 0
) = 0
Characteristic equation =
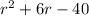
=
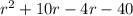
= r(r+10) - 4(r+10)
= (r-4)(r+10)
r1 = 4 and r2= -10
y = e^4x and y = e^-10x
the equation will be C1e^4x + C2e^-10x