Answer:
53.1 mL NaOH
Step-by-step explanation:
The equivalence point of a titration is the point at which an equal amount of moles exists in each solution.
Let's start by writing a chemical equation for this reaction. Using the compounds in the reaction, HCl and NaOH, we can create the following equation:
We have one very important formula that we want to use when dealing with titrations:
- where V = volume (L)
- n = number of moles
- M = molarity
Let's start by finding the number of moles of HCl that is in this reaction using this formula. We have the molarity of HCl and volume of HCl.
Plug in 0.340 for M and 0.0250 L for V. Note that we are given the volume of HCl in mL, but we want to convert to L before using the formula.
Let's convert this number of moles to scientific notation for better readability.
Now that we've found the number of moles of HCl, let's use the coefficients of the compounds in the chemical equation in order to determine the molar ratio between compounds.
We want to determine the moles of NaOH; we can determine this value by using the molar ratio between HCl and NaOH. The coefficients of these substances in the chemical equation are both 1, so we can multiply the moles of HCl by:
Now, we have two variables for NaOH in the formula:
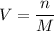
We have the variables n (which we solved for) and M (which we were given). We are trying to solve for V, the volume of NaOH required to reach the equivalence point in the titration:
The last step is to convert 0.053125 L to mL:
I kept the answer to 3 significant figures since the question contains calculations involving 3 significant figures.