The missing part of the question is highlighted in bold form as seen below.
In designing an ECG circuit, it is known that at the input site, the ECG signal is about 1 mV and the amplitude of interference is 100mV. We need enlarge the 1 mV ECG signal to 800mV and keep the interference in the output signal within 5% of the ECG signal. Determine the required differential gain, Gd, and CMRR in dB of this ECG amplifier.
Answer:
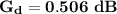
CMRR = 66.02 dB
Step-by-step explanation:
From the given information above:
We can express the formula for calculating the differential gain as:
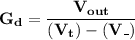
where;
the O/P signal related with e interference is = 800 mV + 5%
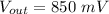
In an ECG circuit system, at one end of i/p, there is a connection to 1 mV & the other end is connected to 800 mV of i/p.
∴
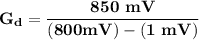
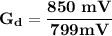
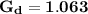
In dB;
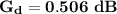
To find the value for the CMRR, we need to determine the Signal to Noise ratio (SNR) by using the formula;
SNR = 1 mV/ 100 mV
SNR = 0.01
SNR = (5%)⁻¹
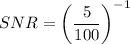
SNR = 20
Finally, we can estimate the Common Mode Ratio (CMRR) can be as:
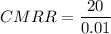
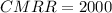
Thus, expressing our answer in dB; we have:
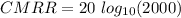
CMRR = 66.02 dB