Answer:
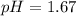
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello.
In this case, since the reaction between the sulfuric acid and the potassium hydroxide is:
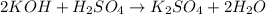
We can see a 2:1 mole ratio between them, thus, we compute the moles of acid and base that are present in the solution by using the employed volume and its concentration:
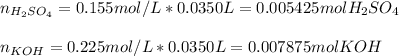
Next, we use the 2:1 mole ratio to compute the consumed moles of acid:
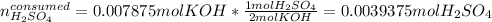
It means that the leftover of sulfuric acid is:
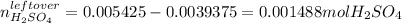
Therefore, since sulfuric acid is a strong acid, the pH is defined in terms of its concentration which is actually equal to the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution, which is computed considering the total additive volume:
![[H^+]=[H_2SO_4]=(0.001488mol)/(0.070L)=0.02125M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/5j4jv8oe03vn3f6ua6suzd6dgao6vf5raz.png)
So the pH turns out:
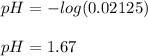
Best regards.