Answer:
Yes , function is continuous in [0,2] and is differentiable (0,2) since polynomial function are continuous and differentiable
Explanation:
We are given the Function
f(x) =
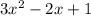
The two basic hypothesis of the mean valued theorem are
- The function should be continuous in [0,2]
- The function should be differentiable in (1,2)
upon checking the condition stated above on the given function
f(x) is continuous in the interval [0,2] as the functions is quadratic and we can conclude that from its graph
also the f(x) is differentiable in (0,2)
f'(x) = 6x - 2
Now the function satisfies both the conditions
so applying MVT
6x-2 = f(2) - f(0) / 2-0
6x-2 = 9 - 1 /2
6x-2 = 4
6x=6
x=1
so this is the tangent line for this given function.